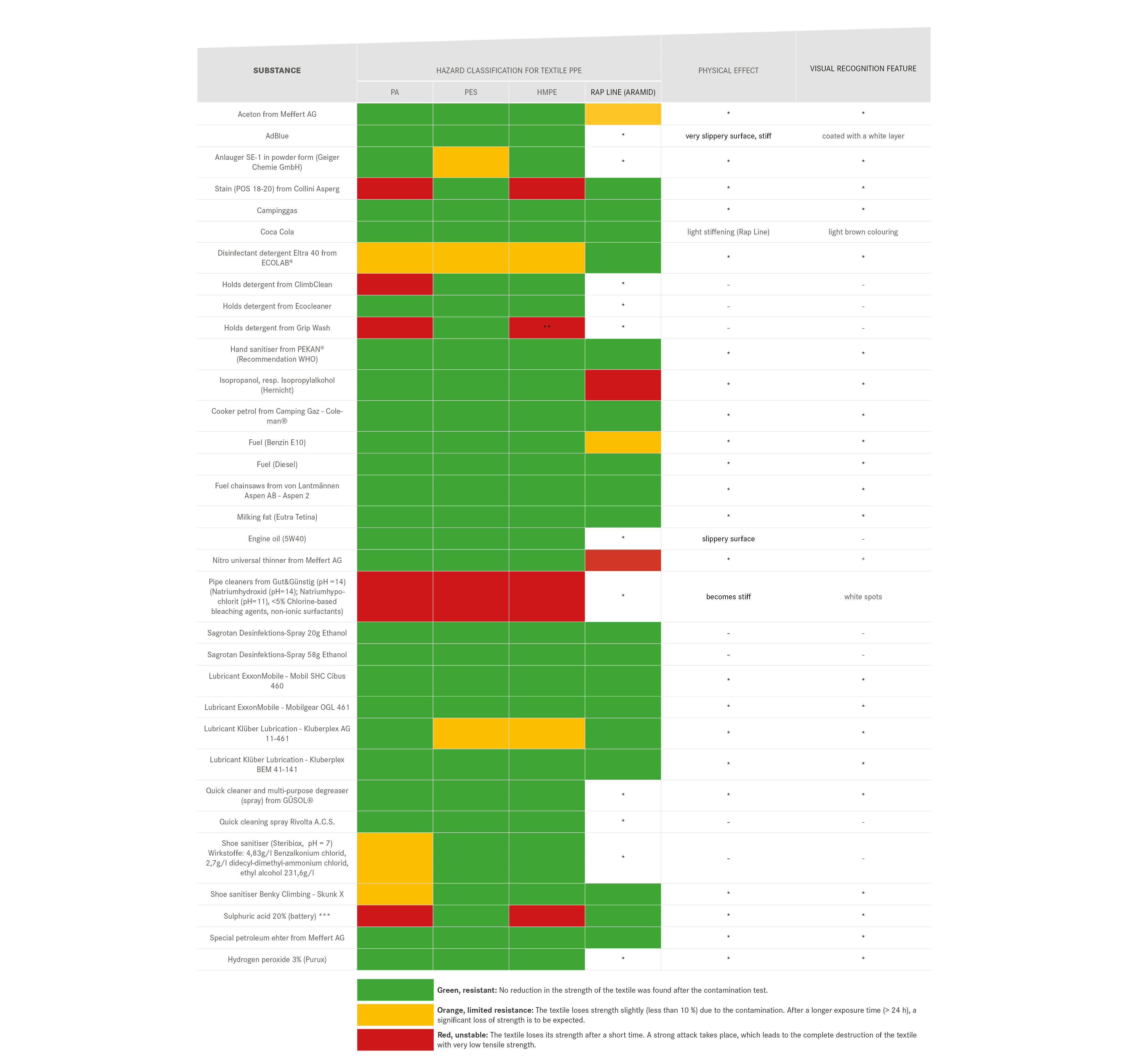
We are endeavouring to gradually expand the table in order to complete the list of items that can come into contact with PPE and their chemical effects on PPE. Be careful when categorising the effects of substances:
- The physical impact of chemicals can also have a major impact on their durability, as in the case of contamination of a core-shell construction. The penetration of the chemical into the sheath braid, but not into the core braid, can stiffen the sheath. This stiffening can lead to a displacement of the sheath in relation to the core under mechanical load or to premature breakage of the sheath if it falls over an edge.
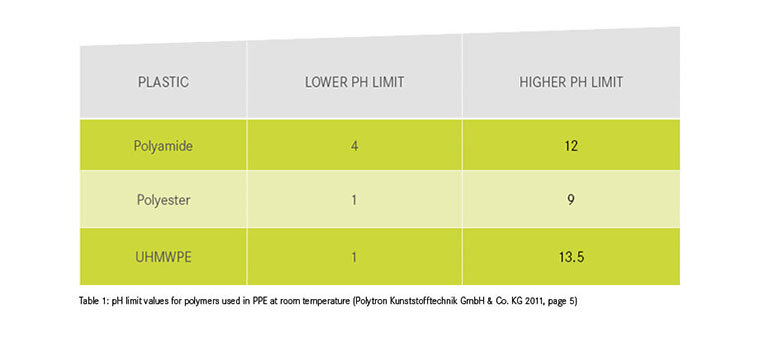
- Beware of different susceptibility of materials! The material information provided by manufacturers refers to the main component of the textile. Dyneema slings, for example, consist to a certain extent of polyamide, which can cause the textile composite to fail without the Dyneema being affected. As long as the exact material composition is not known, PPE must be discarded after chemical contamination with a red-labelled substance.
Conclusion
Table 2 is a list of substances to be assessed as particularly critical and does not represent the release of substances assessed as green or orange. In general, contact of PPE with chemicals of all kinds should be avoided as far as possible, as the interrelationships are complex and not easy to assess. For this reason, textile PPE in particular should be checked for discolouration of unknown origin or areas with an unusual feel and, if in doubt, disposed of. PPE should always be stored separately from liquids or chemicals.
Bibliography
Koller, S.: Säureeinfluss auf Textilmaterial im Bergsport und deren Nachweisbarkeit, degree dissertation.
Polytron Kunststofftechnik GmbH & Co. KG (2011): Chemikalienbeständigkeit. Available online >