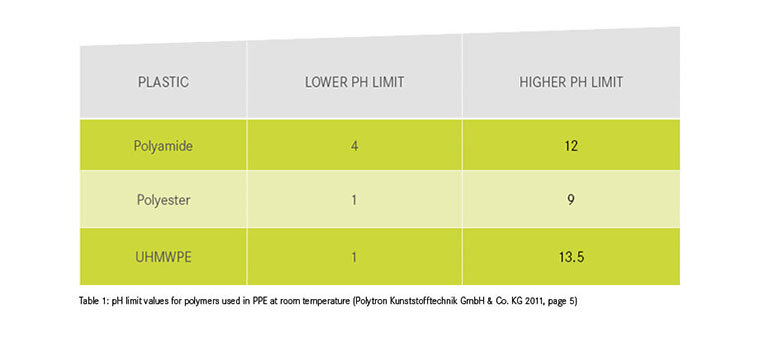
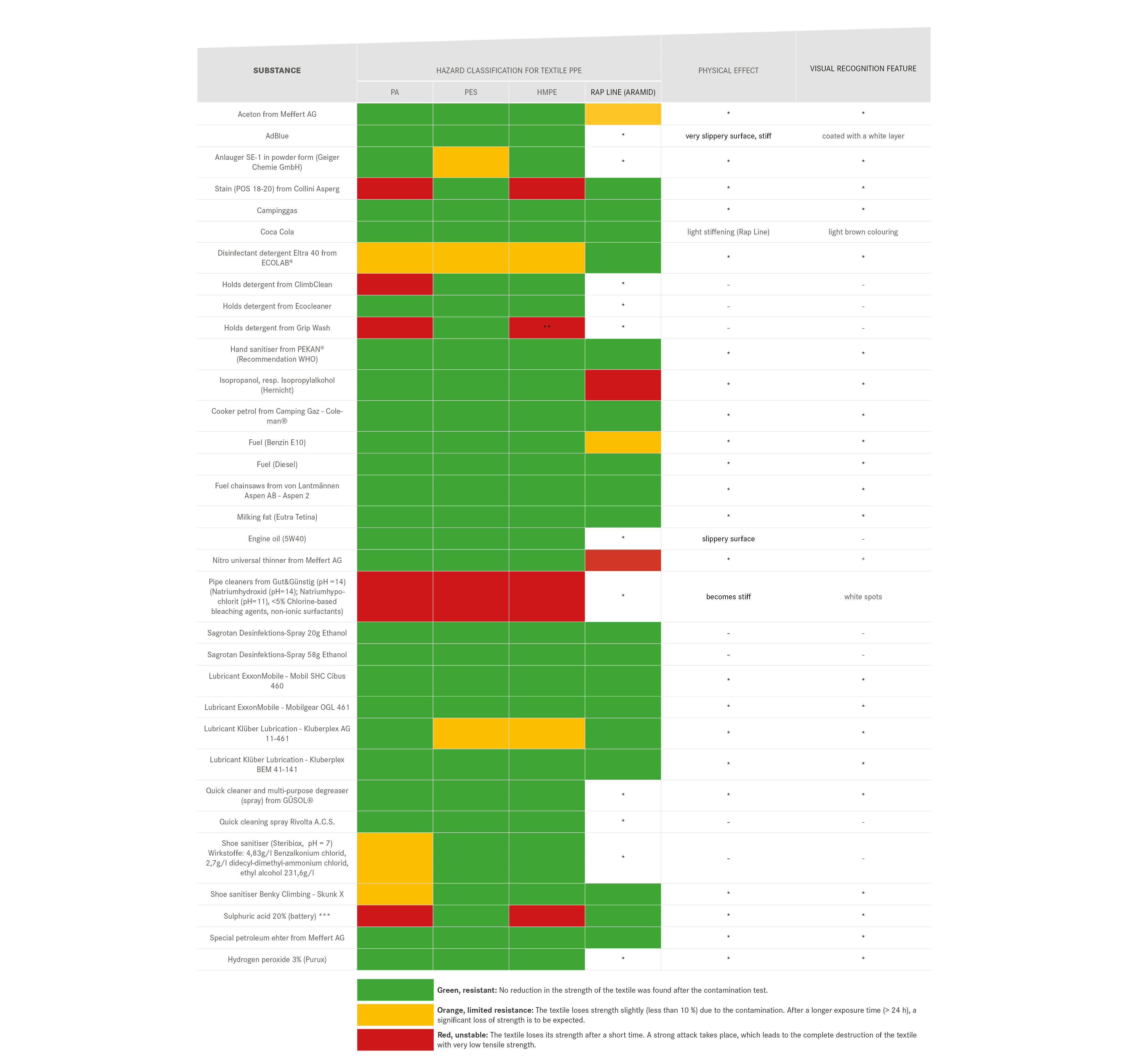
We are endeavoring to expand this table to provide an overview of other substances and their chemical effects on textile PPE. However, caution is required when classifying the effects of substances:
- the physical effect of chemicals can also have a major impact on their durability, as in the case of contamination of a kernmantle design. A stiffening of the sheath can be caused if the chemical penetrates into the sheath braid without penetrating into the core. Under mechanical load this stiffening can lead to a displacement of the sheath or to premature breakage of the sheath when falling over an edge.
- Dyneema slings include some polyamide, which allows the textile composite to fail without the Dyneema deteriorating. The Dyneema threads are torn from the composite and thus can no longer sustain their maximum tensile strength. Therefore, even in the event of contamination with a chemical that is harmless to UHMWPE, caution is required and PPE should be discarded as a precaution.
Conclusion
The effect of chemical substances on PPE is complex and not easy to assess. Therefore, contact between PPE and chemical substances should generally be avoided.
Even though some chemicals are only harmful for certain materials, PPE should be discarded in the event of contamination with strong acids and bases, e.g. hydrochloric acid, grip or pipe cleaners—regardless of the textiles involved.
Moreover, this list is only exemplary and when classifying other substances it is essential to take into account that the components and concentrations of mixtures of substances cannot always be determined.
Bibliography
Koller, S.: Säureeinfluss auf Textilmaterial im Bergsport und deren Nachweisbarkeit, degree dissertation.
Polytron Kunststofftechnik GmbH & Co. KG (2011): Chemikalienbeständigkeit. Available online >